这是你需要的代码,书籍中到处都要这个 train_ch3函数。train_ch3函数又依赖其他多个函数,我这里一次性给你,方便你学习。
# 给定预测概率分布y_hat,当我们必须输出硬预测(hard prediction)时,我们通常选择预测概率最高的类.
# 许多应用都要求我们做出选择.
# 如Gmail必须将电子邮件分类为"Primary(主要邮件)","Social(社交邮件)","Updates(更新邮件)"或"Forums(论坛邮件)".
# Gmail做分类时可能在内部估计概率,但最终它必须在类中选择一个.
# 当预测与标签分类y一致时,即是正确的.分类精度即正确预测数量与总预测数量之比.
# 虽然直接优化精度可能很困难(因为精度的计算不可导),但精度通常是我们最关心的性能衡量标准,我们在训练分类器时几乎总会关注它.
# 为了计算精度,我们执行以下操作.首先,如果y_hat是矩阵,那么假定第二个维度存储每个类的预测分数.
# 使用argmax获得每行中最大元素的索引来获得预测类别.然后将预测类别与真实y元素进行比较.
# 由于等式运算符"=="对数据类型很敏感,因此将y_hat的数据类型转换为与y的数据类型一致.
# 结果是一个包含0(错)和1(对)的张量.最后,求和会得到正确预测的数量.
def accuracy(y_hat,y): #@save
"""计算预测正确的数量"""
if len(y_hat.shape)>1 and y_hat.shape[1] > 1:
y_hat = y_hat.argmax(axis=1)
cmp = y_hat.type(y.dtype) == y
return float(cmp.type(y.dtype).sum())
# 第一个样本的预测类别是2(该行的最大元素为0.6,索引为2),这与实际标签0不一致.
# 第二个样本的预测类别是2(该行的最大元素为0.5,索引为2),这与实际标签2一致.
# 因此,这两个样本的分类精度率为0.5.
print(accuracy(y_hat,y)/len(y)) # 0.5
# 使用程序类
class Accumulator: #@save
"""在n个变量上累加"""
def __init__(self,n):
self.data=[0.0]*n
def add(self, *args):
self.data = [a+float(b) for a,b in zip(self.data, args)]
def reset(self):
self.data = [0.0] + len(self.data)
def __getitem__(self,idx):
return self.data[idx]
# 对于任意数据迭代器data_iter可访问的数据集,可以评估在任意模型net的精度.
def evaluate_accuracy(net,data_iter): #@save
"""计算在指定数据集上模型的精度"""
if isinstance(net,torch.nn.Module):
net.eval() # 将模型设置为评估模式
metric = Accumulator(2) # 正确预测数,预测总数
with torch.no_grad():
for X,Y in data_iter:
metric.add(accuracy(net(X),Y),Y.numel())
return metric[0]/metric[1]
print(evaluate_accuracy(net,test_iter)) # 0.0497,每次都会变.
# 训练
def train_epoch_ch3(net,train_iter,loss,updater): #@save
"""训练模型一个迭代周期"""
# 将模型设置为训练模式
if isinstance(net,torch.nn.Module):
net.train()
# 训练损失总和,训练准确度总和,样本数
metric = Accumulator(3)
for X,Y in train_iter:
# 计算梯度并更新参数
y_hat = net(X)
l = loss(y_hat, Y)
if isinstance(updater,torch.optim.Optimizer):
# 使用PyTorch内置的优化器和损失函数
# Method 1
updater.zero_grad()
l.mean().backward()
updater.step()
# Method 2
# updater.zero_grad()
# l.backward()
# metric.add(float(l) * len(Y), accuracy(y_hat, Y),
# Y.size().numel())
else:
# 使用定制的优化器和损失函数
l.sum().backward()
updater(X.shape[0])
# Method 2
# metric.add(float(l.sum()),accuracy(y_hat,Y),Y.numel())
# Method 1
metric.add(float(l.sum()),accuracy(y_hat,Y),Y.numel())
return metric[0] / metric[2], metric[1] / metric[2]
# 定义一个在动画中绘制数据的实用程序类Animator
class Animator: #@save
"""在动画中绘制数据"""
def __init__(self, xlabel=None, ylabel=None, legend=None, xlim=None, ylim=None, xscale='linear', yscale='linear', fmts=('-','m--','g--','r:'), nrows=1, ncols=1, figsize=(3.5,2.5)):
# 增量地绘制多条线
if legend is None:
legend = []
d2l.use_svg_display()
self.fig, self.axes = d2l.plt.subplots(nrows,ncols, figsize=figsize)
if nrows * ncols == 1:
self.axes = [self.axes,]
# 使用lambda函数捕获参数
self.config_axes = lambda: d2l.set_axes(
self.axes[0], xlabel, ylabel, xlim, ylim, xscale, yscale, legend)
self.X, self.Y, self.fmts = None, None, fmts
def add(self, x, y):
# 向图标中添加多个数据点
if not hasattr(y, "__len__"):
y = [y]
n = len(y)
if not hasattr(x, "__len__"):
x = [x] * n
if not self.X:
self.X = [[] for _ in range(n)]
if not self.Y:
self.Y = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for i, (a,b) in enumerate(zip(x,y)):
if a is not None and b is not None:
self.X[i].append(a)
self.Y[i].append(b)
self.axes[0].cla()
for x, y, fmt in zip(self.X, self.Y, self.fmts):
self.axes[0].plot(x,y,fmt)
self.config_axes()
display.display(self.fig)
display.clear_output(wait=True)
# 实现一个训练函数,它会在train_iter访问到的训练数据集上训练一个模型net.
# 该训练函数将会运行多个迭代周期(由num_epochs指定).
# 在每个迭代周期结束时,利用test_iter访问到的测试数据集对模型进行评估.
# 将利用Animator类来可视化训练进度.
def train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, updater): #@save
"""训练模型"""
animator = Animator(xlabel='epoch', xlim=[1, num_epochs], ylim=[0.3, 0.9], legend=['train loss', 'train acc', 'test acc'])
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
train_metrics = train_epoch_ch3(net, train_iter, loss, updater)
test_acc = evaluate_accuracy(net, test_iter)
animator.add(epoch+1, train_metrics+(test_acc,))
train_loss, train_acc = train_metrics
print(f'train_loss is {train_loss:.2f}. train_acc is {train_acc:.2f}. test_acc is {test_acc:.2f}.')
assert train_loss < 0.5, train_loss
assert train_acc <= 1 and train_acc > 0.7, train_acc
assert test_acc <= 1 and test_acc > 0.7, test_acc
# 作为一个从零开始的实现,使用文档中定义的小批量随机梯度下降来优化模型的损失函数,设置学习率为0.1.
lr = 0.1
def updater(batch_size):
return d2l.sgd([W,b],lr, batch_size)
# 训练模型10个迭代周期.请注意,迭代周期(num_epochs)和学习率(lr)都是可调节的超参数.
# 通过更改它们的值,可以提高模型的分类精度.
num_epochs = 10
train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, cross_entropy, num_epochs, updater)
非常感谢您的解答!!!稍后我去试试。
Blockquote
如果在colab中该怎么解决这个问题?在colab上怎么找到这些依赖文件
Colab需要使用命令先安装d2l
!pip install d2l
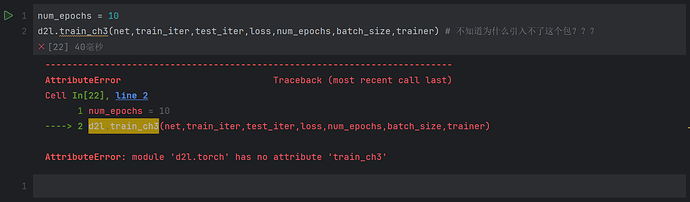
我是直接执行的!pip install git+https://github.com/d2l-ai/d2l-en@release,安装完成之后在代码运行当中就会提示没有train_ch3这个函数
用train_ch6也可以。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。