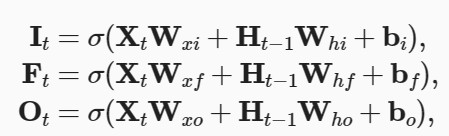为什么可以缓解梯度爆炸呢,这里不是非常懂
这里的vocab_size指的是词向量的维度吧?
对第4问没懂。“ 那么为什么隐状态需要再次使用tanhtanh函数来确保输出值范围在(−1,1)(−1,1)之间呢?”,这里隐状态有用tanh函数吗?隐状态H的计算公式里不是只用了一次tanh作用在C_t上吗?
候选记忆元用tildeC表示,记忆元用C表示。
- 首先来回答您关于隐状态是否使用了 tanh()函数的疑问。
Ht = Hadamard(Ot,tanh(Ct)),(Hadamard就是逐元素的乘积)
在这里,隐状态表示为了Ot和tanh(Ct)的Hadamard积,这里所说的“隐状态再次使用了 tanh() 函数”其实指的就是这里的记忆元使用了tanh()函数,因为记忆元Ct使用了 tanh()函数,且其和Ot的Hadamard积的最终表示结果就是Ht,故可以理解为Ht使用了 tanh() 函数。 - 关于这一个问题的具体解答,是这样的:
虽然候选记忆元 tildeC 使用了tanh()函数,但是求Ct的方式是这样的
Ct = Hadamard(Ft, Ct-1) + Hadamard(It, tildeCt)
可以很容易看出,例如当Ft和It均取1,且Ct-1和tildeCt也均取1时,结果为2,超出了(-1, 1)范围。故最后还需使用tanh()函数在求Ht的过程中使其回到(-1, 1)。
想知道如何从lstm 进化到gru的?从目前来看使用reset, update gates基本上已经达到类似效果
为什么要限制在(-1,1)?有什么好处呢?。。。。
练习第2题生成合适单词该怎么处理呢?predict_ch8返回的是vocab.idx_to_token[i], 如何优化以返回合适单词呢?
我猜测是因为两者效果上类似,但是gru比lstm简单(删减掉了记忆元部分)?
这应该是防止爆炸吧,绝对值小于1的数相乘,得到的绝对值肯定小于自身呀 ![]()
我觉得可能是加入遗忘门的缘故,遗忘门保留了过去的记忆元,使之不会产生梯度爆炸
9.2.1.1里面 什么叫做输入为d, 是d维的意思吗
![]()
我在想num_steps与vocab_size值是不是相等的,还有输入数d是啥意思,不懂。
因为在代码里面在训练的时候还是调用了Ch8的训练函数train_epoch_ch8,里面就有做梯度裁剪的操作,所以就可以缓解梯度爆炸。
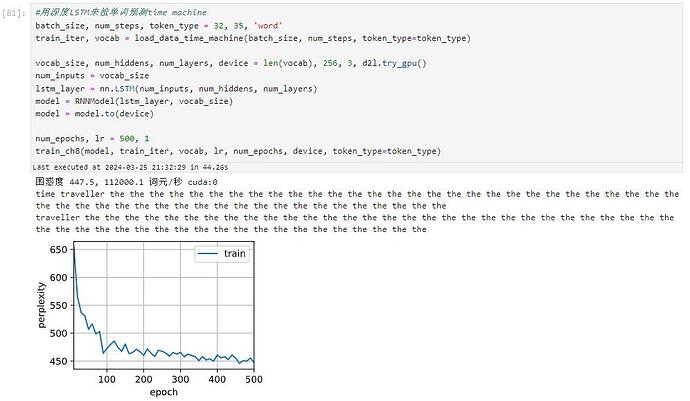
按词来预测的话,只需要增加一系列参数token_type,直到tokenize函数,并且在predict_ch8中判断如果token_type==‘word’,那么output就不用空字符来join,而是换成空格来join(因为单词之间要用空格分隔)就可以了,但效果不好,输出出来基本是无意义的。
"按词预测"
def load_corpus_time_machine(max_tokens=-1,token_type='word'): #@save
"""返回时光机器数据集的词元索引列表和词表"""
lines = d2l.read_time_machine()
tokens = d2l.tokenize(lines, token_type)
vocab = d2l.Vocab(tokens)
# 因为时光机器数据集中的每个文本行不一定是一个句子或一个段落,
# 所以将所有文本行展平到一个列表中
corpus = [vocab[token] for line in tokens for token in line]
if max_tokens > 0:
corpus = corpus[:max_tokens]
return corpus, vocab
class SeqDataLoader: #@save
"""加载序列数据的迭代器"""
def __init__(self, batch_size, num_steps, use_random_iter, max_tokens, token_type='word'):
if use_random_iter:
self.data_iter_fn = d2l.seq_data_iter_random
else:
self.data_iter_fn = d2l.seq_data_iter_sequential
self.corpus, self.vocab = load_corpus_time_machine(max_tokens,token_type)
self.batch_size, self.num_steps = batch_size, num_steps
def __iter__(self):
return self.data_iter_fn(self.corpus, self.batch_size, self.num_steps)
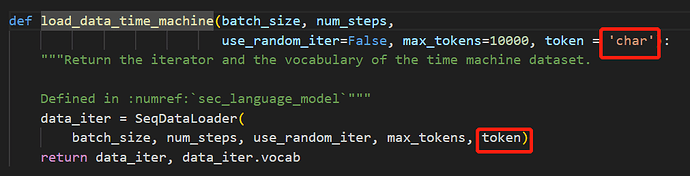
def load_data_time_machine(batch_size, num_steps, #@save
use_random_iter=False, max_tokens=10000, token_type='word'):
"""返回时光机器数据集的迭代器和词表"""
data_iter = SeqDataLoader(
batch_size, num_steps, use_random_iter, max_tokens, token_type)
return data_iter, data_iter.vocab
token_type = "word"
batch_size, num_steps = 32, 10
train_iter, vocab = load_data_time_machine(batch_size, num_steps, token_type = token_type)
vocab_size, num_hiddens, device = len(vocab), 256, d2l.try_gpu()
print("vocab",vocab.idx_to_token,len(vocab))
def predict_ch8(prefix, num_preds, net, vocab, device, token_type = 'word'): #@save
"""在prefix后面生成新字符"""
if token_type=='word':
prefix = prefix.split()
state = net.begin_state(batch_size=1, device=device)
outputs = [vocab[prefix[0]]]
get_input = lambda: torch.tensor([outputs[-1]], device=device).reshape((1, 1))
for y in prefix[1:]: # 预热期
_, state = net(get_input(), state)
outputs.append(vocab[y])
for _ in range(num_preds): # 预测num_preds步
y, state = net(get_input(), state)
outputs.append(int(y.argmax(dim=1).reshape(1)))
if token_type=='word':
return ''.join([vocab.idx_to_token[i]+' ' for i in outputs])
else:
return ''.join([vocab.idx_to_token[i] for i in outputs])
def train_ch8(net, train_iter, vocab, lr, num_epochs, device,
use_random_iter=False, token_type='word'):
"""训练模型(定义见第8章)"""
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', ylabel='perplexity',
legend=['train'], xlim=[10, num_epochs])
# 初始化
if isinstance(net, nn.Module):
updater = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr)
else:
updater = lambda batch_size: d2l.sgd(net.params, lr, batch_size)
predict = lambda prefix: predict_ch8(prefix, 50, net, vocab, device,token_type=token_type)
# 训练和预测
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
ppl, speed = d2l.train_epoch_ch8(
net, train_iter, loss, updater, device, use_random_iter)
if (epoch + 1) % 10 == 0:
print(predict('time traveller'))
animator.add(epoch + 1, [ppl])
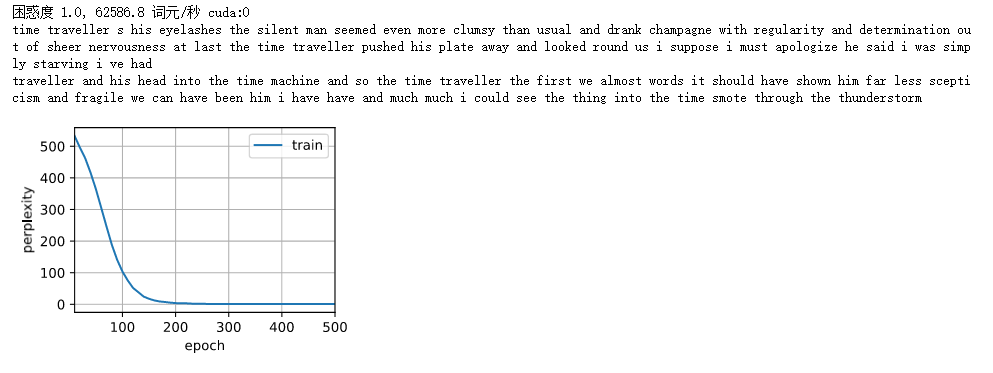
print(f'困惑度 {ppl:.1f}, {speed:.1f} 词元/秒 {str(device)}')
print(predict('time traveller'))
print(predict('traveller'))
num_epochs, lr = 500, 1
num_inputs = vocab_size
lstm_layer = nn.LSTM(num_inputs, num_hiddens)
model = d2l.RNNModel(lstm_layer, len(vocab))
model = model.to(device)
train_ch8(model, train_iter, vocab, lr, num_epochs, device,token_type='word')
我这里把num_steps改为10,输出是有意义的。但是vocab长度很大。
我觉得是因为,候选记忆虽然是通过一次tanh得到,但是后来它又与输入门进行了一个点积操作,有可能数值会大于1

 脑子里面还记得多少数据
脑子里面还记得多少数据